[最も欲しかった] dural venous sinuses simple diagram 208030
Anatomy, Imaging and Surgery of the Intracranial Dural Venous Sinuses, 1st Edition Editor R Shane Tubbs This firstofitskind volume focuses on the anatomy, imaging, and surgery of the dural venous sinuses and the particular relevance to neurosurgery and trauma surgery Knowledge of the fine clinical anatomy involved in neurosurgery andDural venous sinuses Dural venous sinuses are venous channels located intracranially between the two layers of the dura mater (endosteal layer and meningeal layer) They can be conceptualised as trapped epidural veins Unlike other veins in the body, they run alone, not parallel to arteries Furthermore, they are valveless, allowing forMar 09, 16 · The dural venous sinuses lie between the periosteal and meningeal layers of the dura mater They are best thought of as collecting pools of blood, which drain the central nervous system, the face, and the scalp All the dural venous sinuses ultimately drain into the internal jugular vein Unlike most veins of the body, the dural venous sinuses
Cavernous Sinus Neuroangio Org
Dural venous sinuses simple diagram
Dural venous sinuses simple diagram-Jun 8, 19 Important exam questions on anatomy of head and neck enumerate, draw labelled diagrams, short notes, long questions and applied anatomy questions Today Explore When autocomplete results are available use up and down arrows to review and enter to select Touch device users, explore by touch or with swipe gesturesFeb 16, 17 · Dural venous sinuses are venous channels that are present usually the two layers of dura mater They are lined by endothelium They do not have muscle in their walls They have no valves They drain blood from Brain;




Big Sexy Brain
Oct 01, 06 · Our practical analysis of CT venography is standardized and involves the following steps First, twodimensional (2D) MPR images are used to visualize dural venous sinuses and cerebral veins, with adequate window level and width Windows setting are wider than those typically used for brain parenchyma (, ,, 21 )This video provides a walkthrough of the dural venous sinuses (eg transverse sinus, cavernous sinus) You can follow along using our free written guide witAug 01, 11 · MATERIALS AND METHODS We measured HUs in a region of interest within the confluence of dural venous sinuses in 166 unenhanced head CTs and correlated these data with HCT and HGB values in male and female patients aged 2 to 100 years We then compared these data with similar measurements in 8 patients with recent venous sinus thrombosis Twotailed t
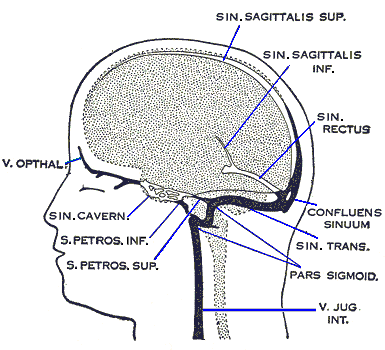
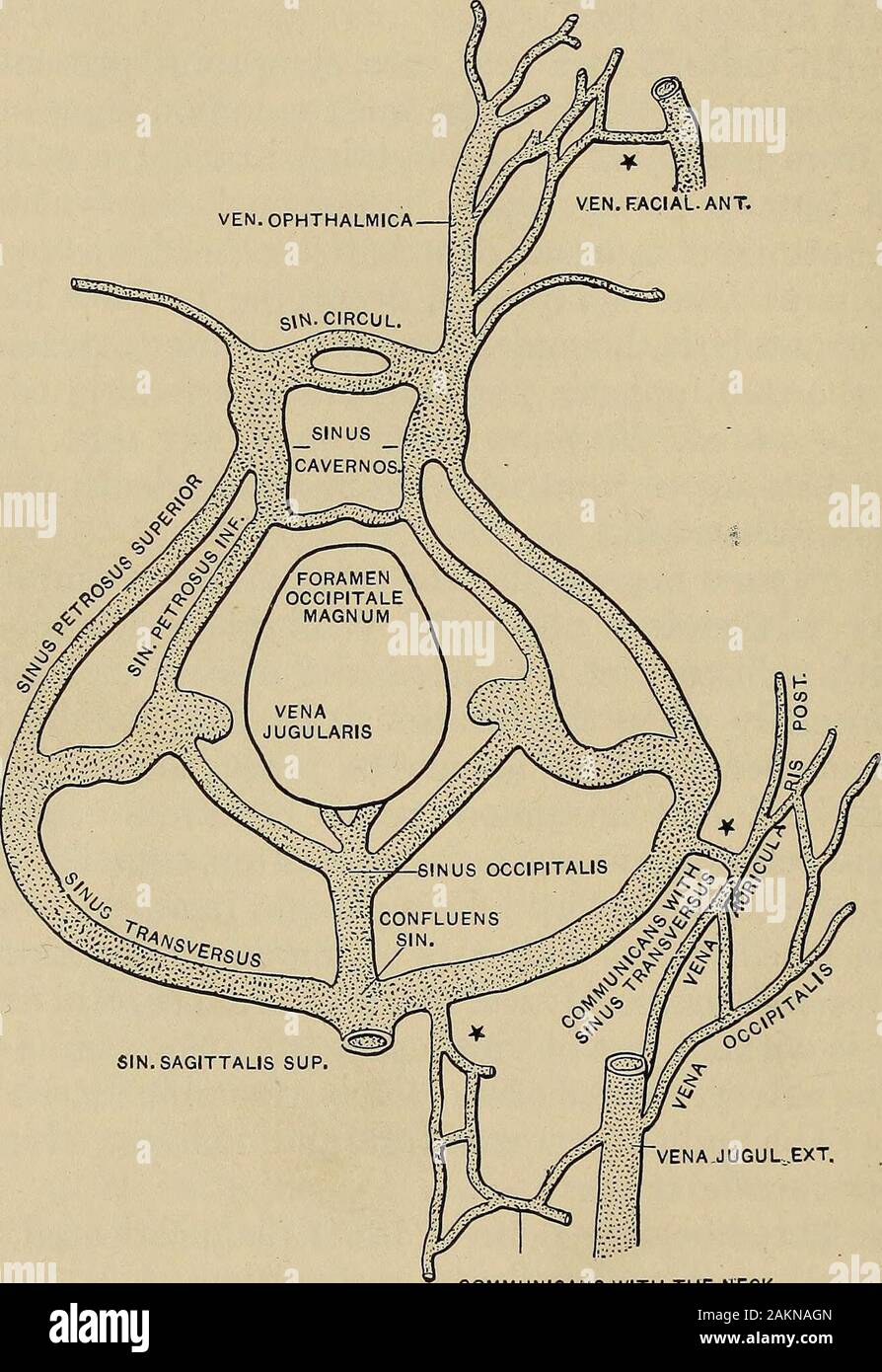
In the lateral wall of the sinus lies 111,1V, V1,V2 The superior petrosal sinus drains blood to the transverse sinus The inferior petrosal sinus drains blood directly to the sigmoid sinus The emissary veins connect veins from the scalp to the dural venous sinuses, these open up a significant route by which infection may spreadJul 17, 13 · Dural sinuses 1 Pronograde Quadruped vertebrate Orthograde – plantigrade Biped – erect vertebrate 2 Splanchnocranium Neurocranium Telencephalisation Inversely proportional 3 Blood supply of brain Venous drainage of brain Brain – Internal carotid Vertebral art Choroid plexus Skull – MidMeningeal artInjection of gadolinium in sagittal (a) & coronal (b) planes There is visualization of dural venous sinuses and superficial & deep cerebral veins 1=Superior sagittal sinus, 2= Straight sinus,3=Torcular Herophili,4=Vein of Galen,5=Lateral sinus,6=Sigmoid sinus,7=Internal Jugular
Dural sinus thrombosis (DST) is a condition where a blood clot forms in one of the dural sinuses The dural sinuses are located in your head They drain deoxygenated blood as well as cerebropsinal fluid (CSF) that surrounds your brain, and empties them into the internal jugular vein that takes it back to your heart and lungs to be reoxygenated They are called venous sinusesFeb 12, 18 · Craniotomies that cross a sinus should maximize exposure while minimizing the risk of sinus injury and provide a cosmetically appealing result with simple reconstruction techniques We describe the published techniques for exposing dural venous sinuses, and introduce a new technique for a singlepiece craniotomy exposing the superior sagittalJul 31, 19 · Dural Venous Sinuses Of The Brain Diagram Dural Venous Sinuses Of The Brain Diagram In this image, you will find superior sagittal sinus, falx cerebri, inferior sagittal sinus, straight sinus, cavernous sinus, transverse sinuses, sigmoid sinus, jugular foramen, right internal jugular vein in it Our SECOND youtube film is ready to run
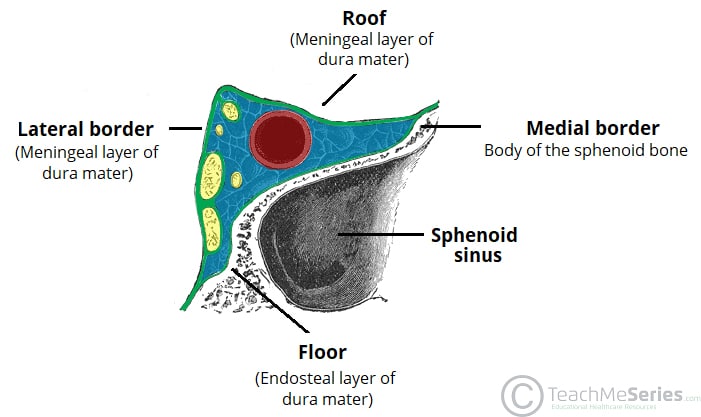



The Cavernous Sinus Contents Borders Thrombosis Teachmeanatomy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/dural-sinuses/MBT9Z5mR2o8TnY2hb131w_Superficial_veins_of_the_brain_lateral_view.png)



Dural Venous Sinuses Anatomy Kenhub
Nov 28, · In fact, they did not observe flow gaps in dominant transverse sinuses or in the rest of the dural venous system, making it imperative to exclude thrombosis before concluding a flow gap The lack of thrombus related signals and use of CEMRV (independent of the flow dynamics) aid in confirming patency of sinuses Figure 13Start studying Dural venous sinuses Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsJun 17, 21 · Dural venous sinuses The human brain has the highest demand for oxygen of any tissue in the human body It receives a vast amount of blood from two systems the internal carotid system anteriorly, and the vertebrobasilar system posteriorly However, there is very little space in the cranial vault to accommodate large amounts of blood
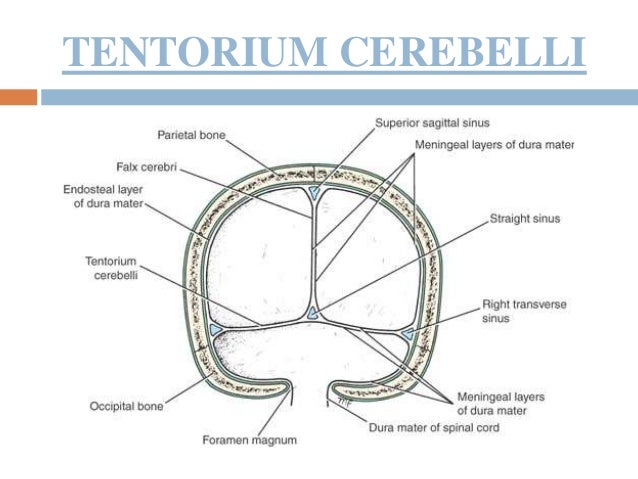



15 Dural Venous Sinuses
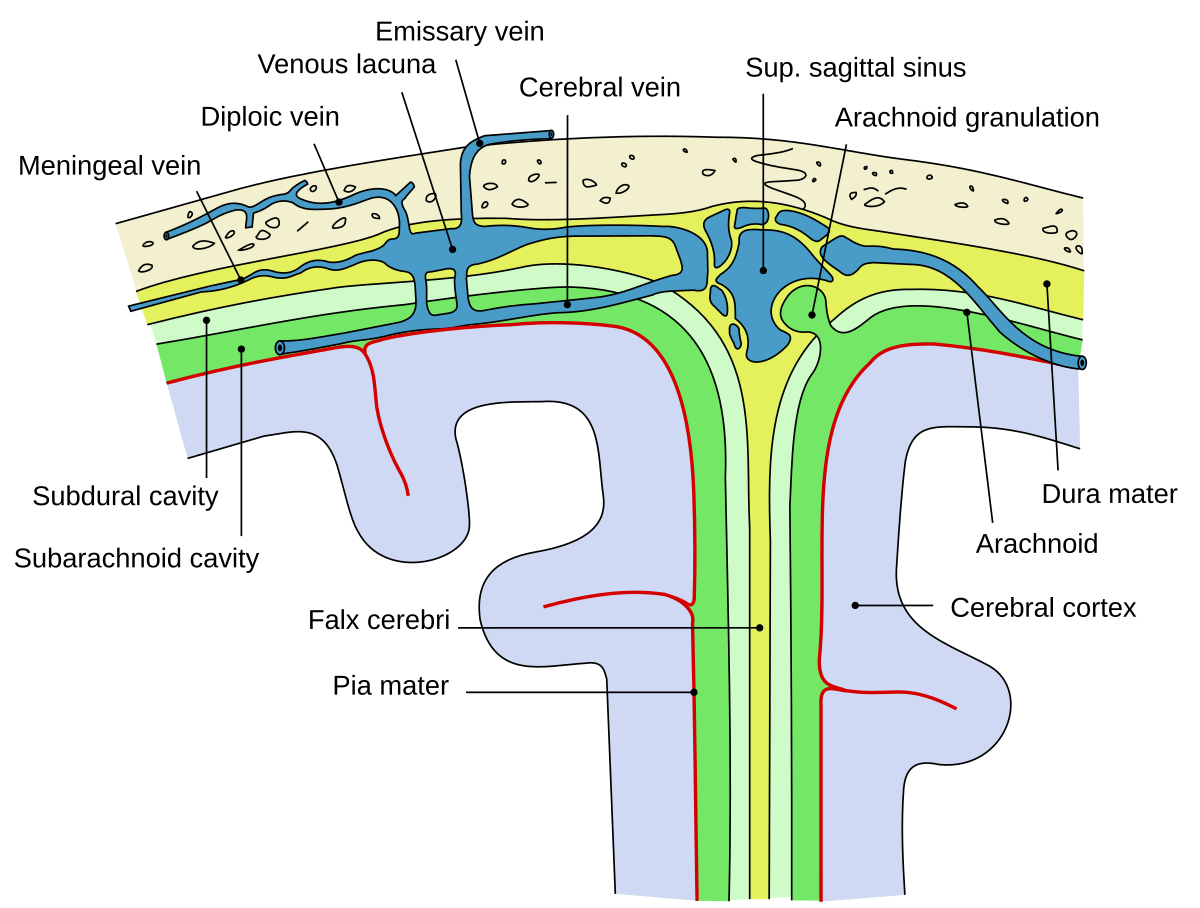



Arachnoid Granulation Wikipedia
Jan 01, 17 · The dural sinuses are large endotheliallined trabeculated channels that collect cerebral blood from the superficial, deep, and posterior fossa and drain into the internal jugular vein at the level of the jugular bulb These sinuses, which lie between the superficial (periosteal) and deep (meningeal) layers of the dura mater, also excrete cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) via arachnoidThe sinuses of the dura mater are venous channels which drain the blood from the brain;Type I dural arterial supply drains anterograde into venous sinus Type II dural arterial supply drains into venous sinus High pressure in sinus results in both anterograde drainage and retrograde drainage via subarachnoid veins Type III dural arterial supply drains retrograde into subarachnoid veins Type I




Improvement In Venous Outflow Following Superior Sagittal Sinus Decompression After A Gunshot Wound To The Head Case Report In Journal Of Neurosurgery Volume 123 Issue 1 15
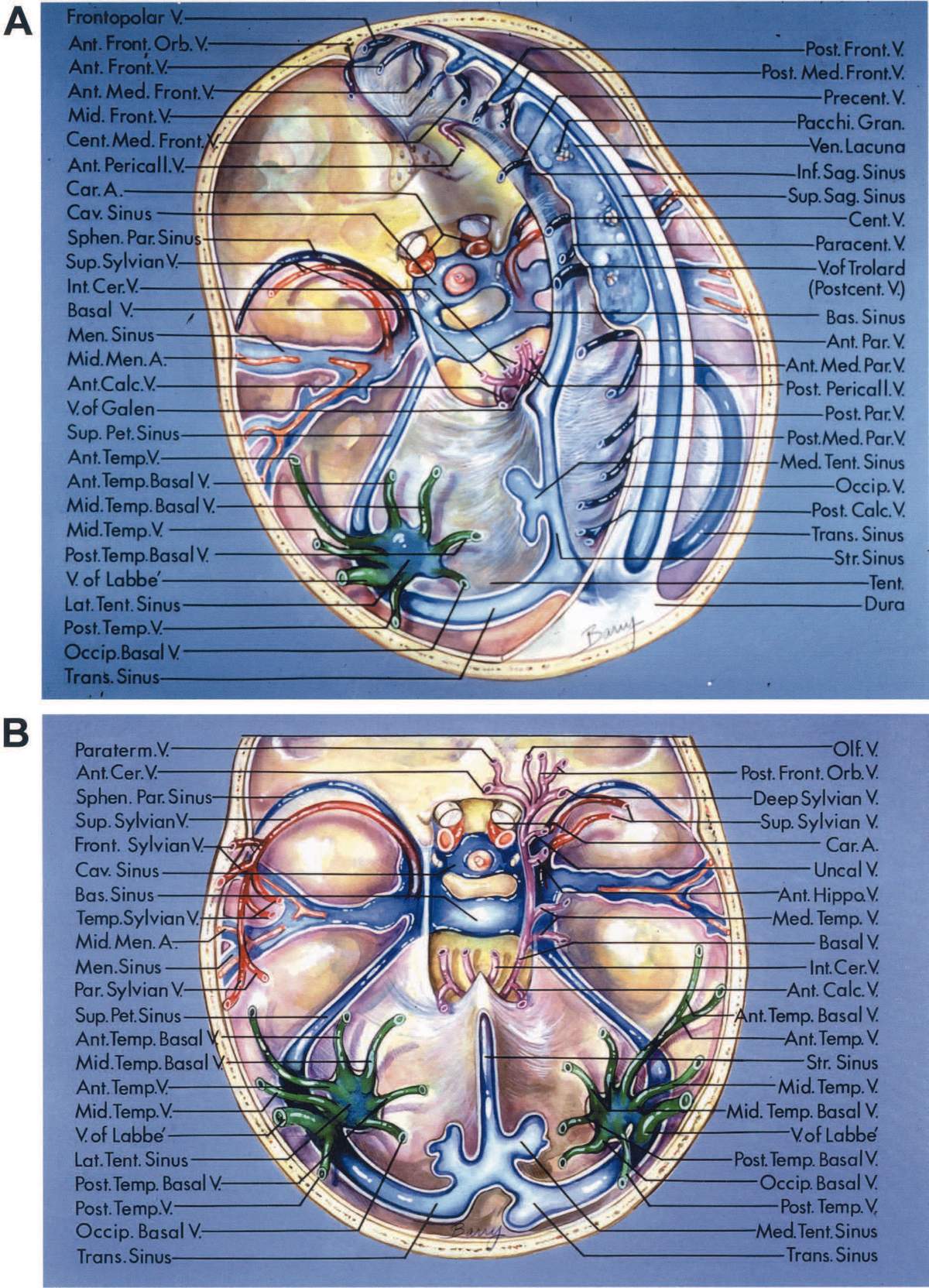



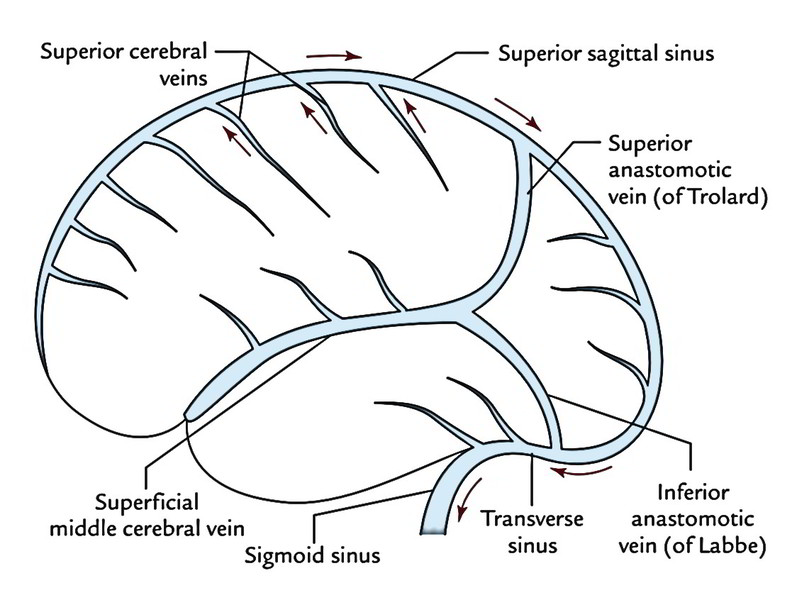
Cerebral Veins The Neurosurgical Atlas
Aug 01, 16 · Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis Venous occlusion presents with a myriad of symptoms with variable severity Sometimes the symptoms are as mild as simple headaches and othertimes they are severe enough to produce confusion, stupor, or even coma, along with paralysis and other focal neurologic deficits Superior sagittal sinus or the dominant transverse sinusMar 07, 16 · Sphenoparietal sinus 7 Petrosquamous sinus 8 Middle meningeal sinus ©DrNMugunthan 8 Cavernous sinus Paired dural venous sinus Situation on each side of body of sphenoid bone Extent Front – superior orbital fissure Behind apex of petrous part of temporal bone ©DrNMugunthan 9Jul 02, 19 · Located between these two layers are channels called dural venous sinuses These veins drain blood from the brain to the internal jugular veins, where it is returned to the heart The meningeal layer also forms dural folds that divide the cranial cavity into different compartments, which support and house various subdivisions of the brain




Pdf Cerebral Vein Thrombosis Misdiagnosed And Mismanaged



Cavernous Sinus Neuroangio Org
The dural venous sinuses (DVS) are venous blood reservoirs located between the 2 layers of the dura mater The absence of lymphatic drainage in the brain places the venous outflow system means that the DVS is critically important This article provides an overview on dual venous sinuses and then focuses on arachnoid granulations, tributariesMar 27, · Dural sinus injury and occlusion can lead to devastating venous infarction and irreversible neurologic deficits, if not handled judiciously Therefore, it is imperative to anticipate, be prepared, remain calm, and be determined to manage dural sinus bleeding wisely Some measures are worth special emphasisSWS is part of a family of neurocutaneous disorders, characterized by abnormalities of ecto and endoderm The cutaneous part is a port wine stain (in CN V distribution) The brain part is described below About 1/3 of patients only have the skin part, 1/3 have only brain, and 1/3 both —
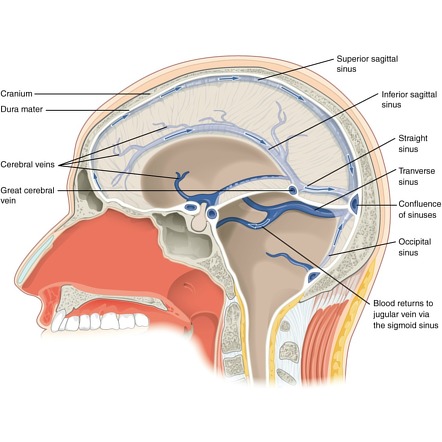



Dural Venous Sinuses Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



Dural Venous Vasculature Intrinsic Dural And Skull Veins Neuroangio Org
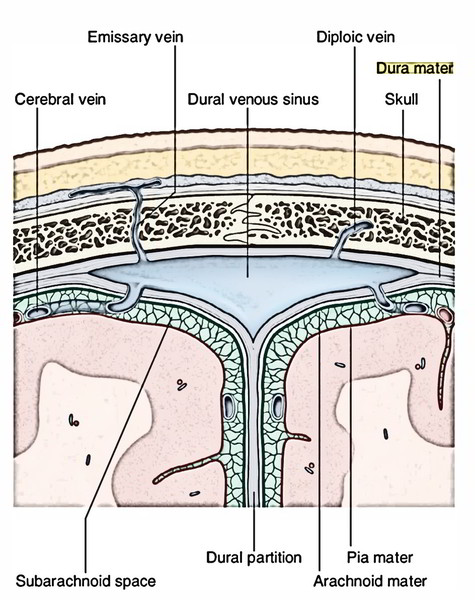
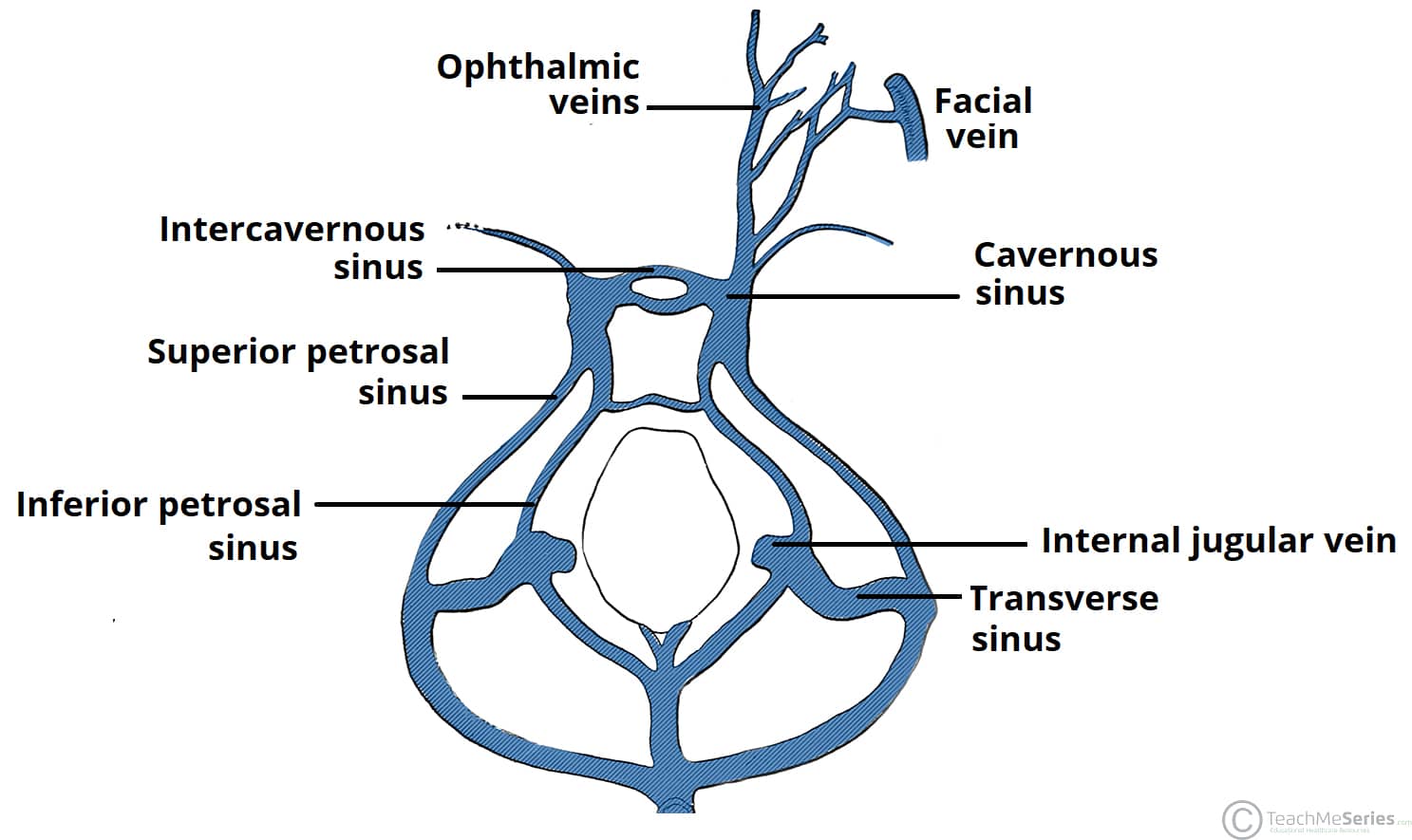
They also drain CSF They communicate with veins outside the cranial cavity via emissary veins NameTHEORY OF DURAL VENOUS SINUS VIDEO https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=Ebw3OwEQKtcTRANS CRIBRIFORM APPROACH VIDEO https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=9v_C94Bwo8s&The cavernous sinuses are 1 cm wide cavities that extend a distance Inferior petrosal sinus directly to the jugular bulb Superior petrosal sinus to the transverse sinus Roof meningeal layer of the dura mater The cavernous sinus is one of the dural venous sinuses of the head Venous blood drains posteroinferiorly to eventually empty into the
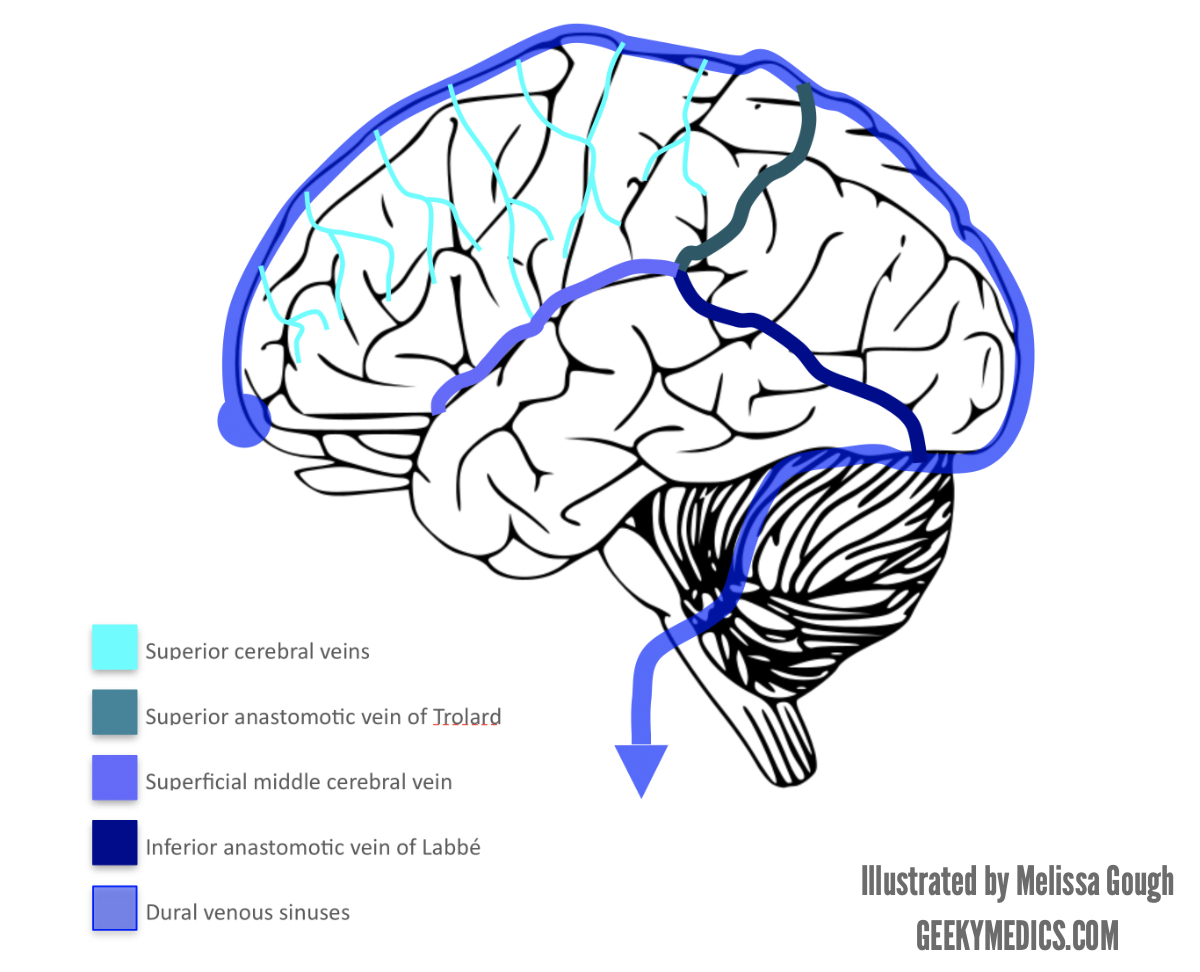



Venous Drainage Of The Brain Anatomy Geeky Medics




Dural Venous Sinuses 3d Anatomy Tutorial Youtube
Aug 08, 18 · Receive venous blood and CSF Receive valveless emissary veins which modulate the blood circulation and keep the equilibrium of venous pressure inside and outside the skull Categorization There are about 21 sinuses They may be classified into 2 types paired and unpaired Categorization of the dural venous sinuses (7 matched and 7 unpaired)They are devoid of valves, and are situated between the two layers of the dura mater and lined by endothelium continuous with that which lines the veins They may be divided into two groups (1) a posterosuperior, at the upper and back part of the skull, and (2) an anteroinferior, at the baseDural venous sinuses are venous channels located intracranially between the two layers of dura mater endosteal layer and meningeal layer The sphenoparietal sinus courses along the free border They are best thought of as collecting pools of blood which drain the central nervous system the face and the scalp
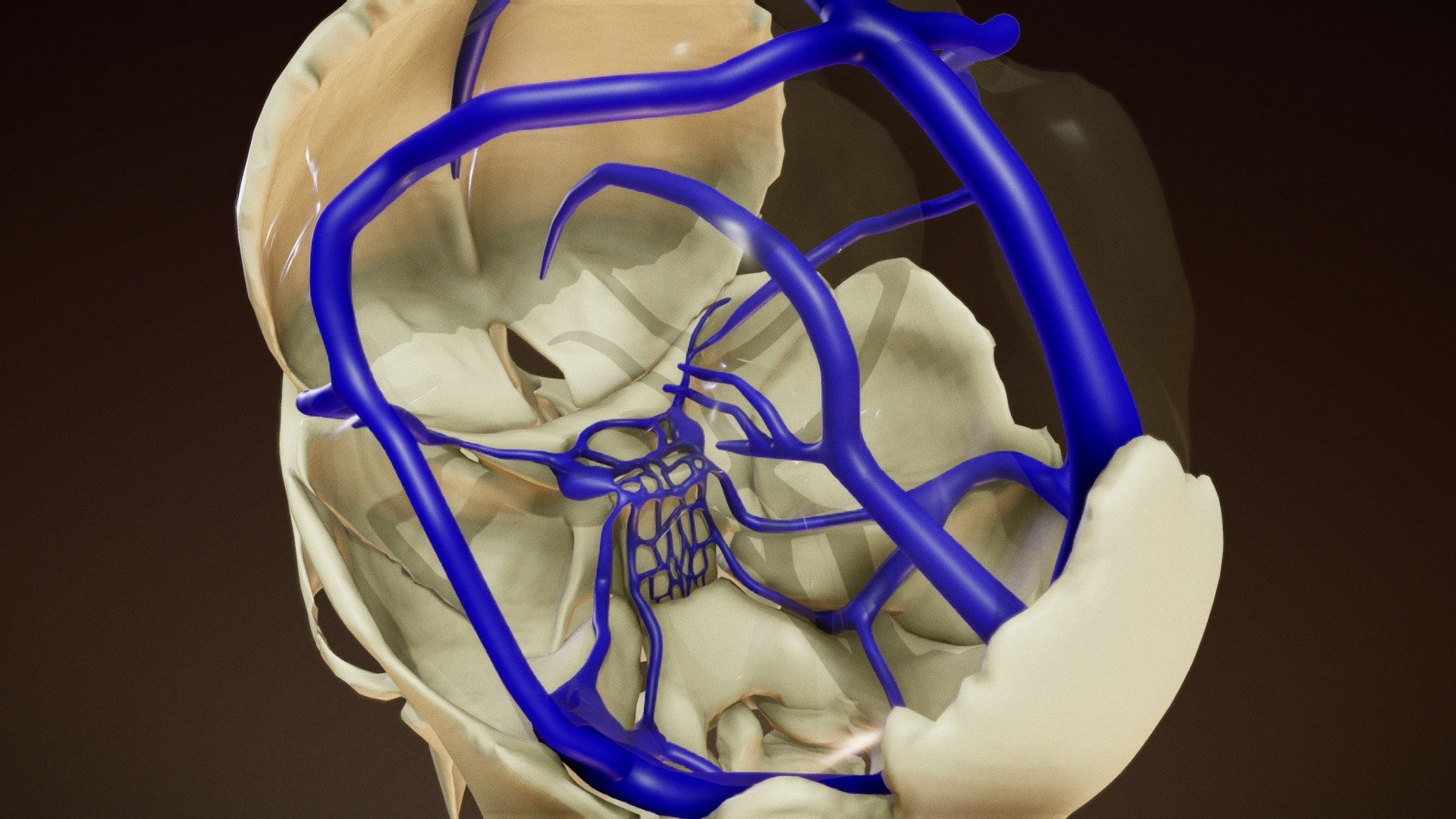



Dural Venous Sinuses Buy Royalty Free 3d Model By Anatomy By Doctor Jana Docjana 07c7b
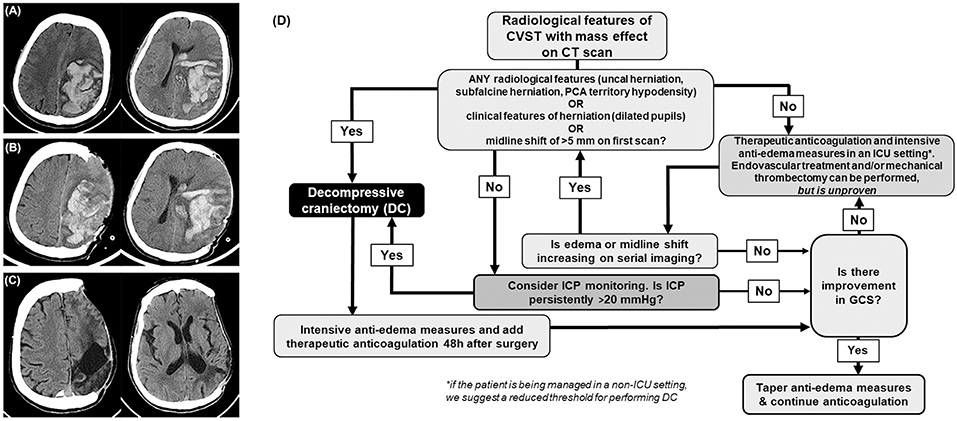



Frontiers Role Of Decompressive Craniectomy In The Management Of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Neurology
Mar 25, 13 · Clinical Relevance Cavernous Sinus The cavernous sinuses are a clinically important pair of dural sinuses They are located next to the lateral aspect of the body of the sphenoid bone This sinus receives blood from the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins, the middle superficial cerebral veins, and from another dural venous sinus;Preferentially, dural sinuses are located at confluence of dural sheaths, such as falx and convexity, or convexity and tentorium However, increased flow can help maintain a dural sinus elsewhere, for example within convexity dura, as shown in above examples Usually these kinds of dural sinuses are recipients of large cortical veinsJun 13, 15 · Dural Venous Sinuses Dural venous sinuses (see Fig 616) are a complex of venous channels that lie between the two layers of dura mater, draining blood from the brain and cranial bones They are lined by endothelium and have no valves;




Inferior Petrosal Sinus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Dural Venous Sinuses Anatomy Kenhub
The dural venous sinuses (also called dural sinuses, cerebral sinuses, or cranial sinuses) are venous channels found between the endosteal and meningeal layers of dura mater in the brain 1 2 They receive blood from the cerebral veins , receive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the subarachnoid space via arachnoid granulations , and mainly empty into the internal jugular veinDural sinus malformation (DSM) is a rare pediatric cerebrovascular malformation, presenting in antenatal or early postnatal life with massive dilation of the dural sinuses Barbosa's 03 seminal paper describes two forms of the disease a midline subtype spanning the confluence of the sinuses with giant dural sinus lakes (socalled 'torcular DSM' (tDSM), the focus of Yang's twoTheir walls are devoid of



Anatomy And Function Of The Dural Venous Sinuses Medical Library




Dural Venous Sinuses Paired And Unpaired Venous Sinuses Anatomy Qa
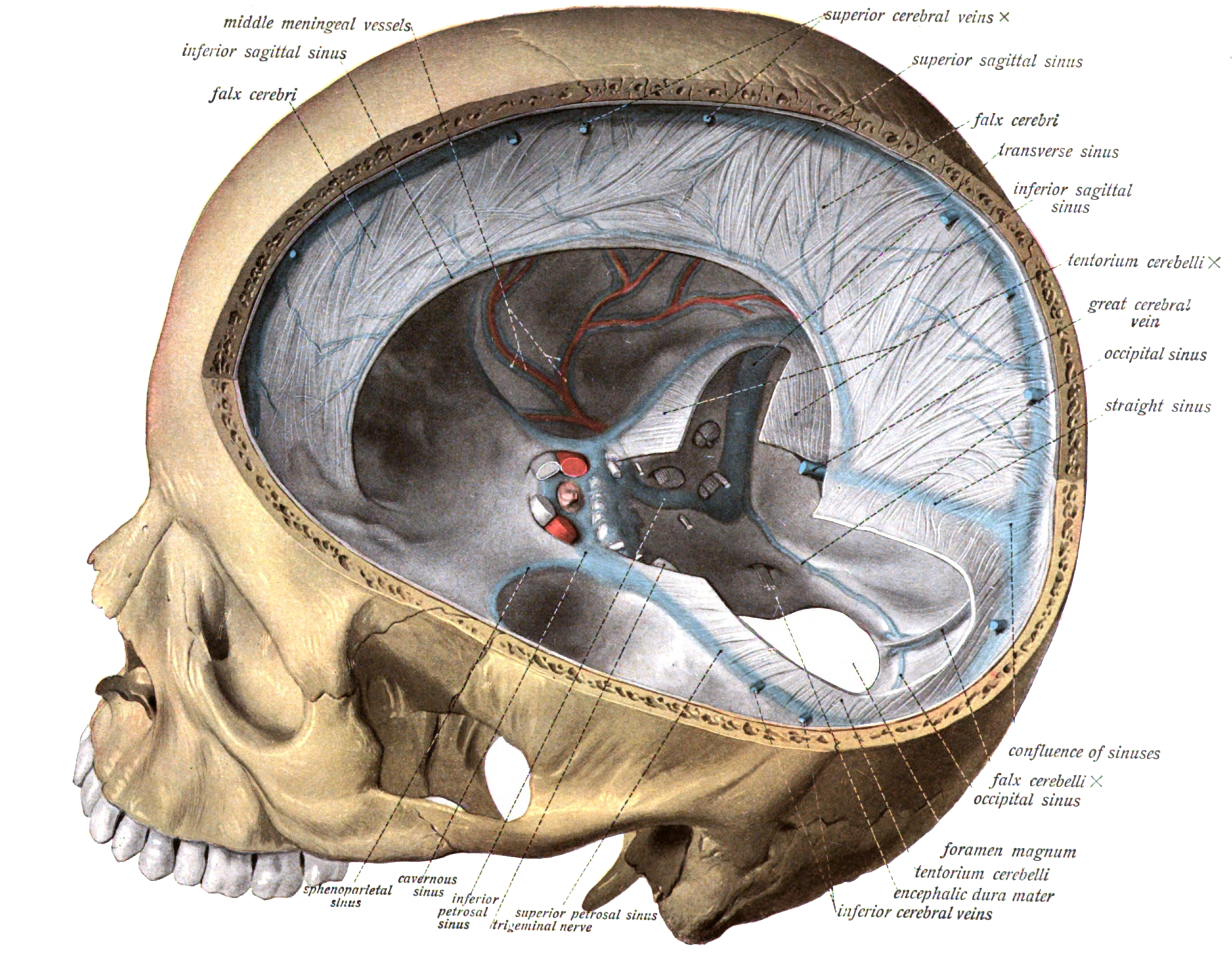
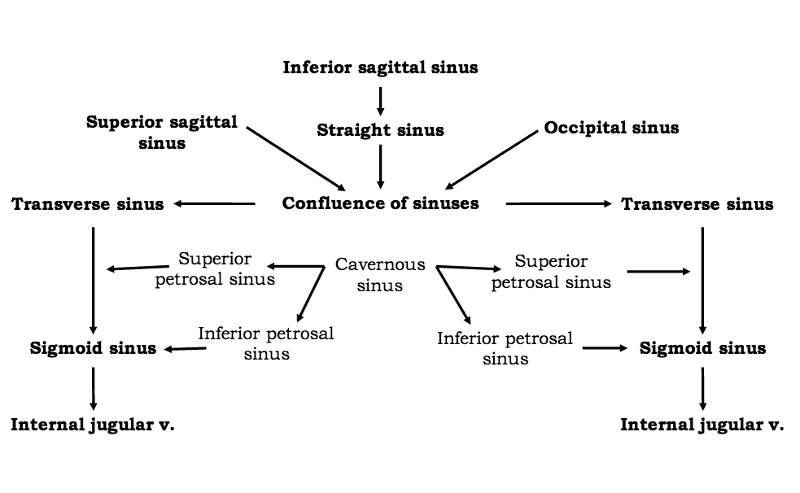
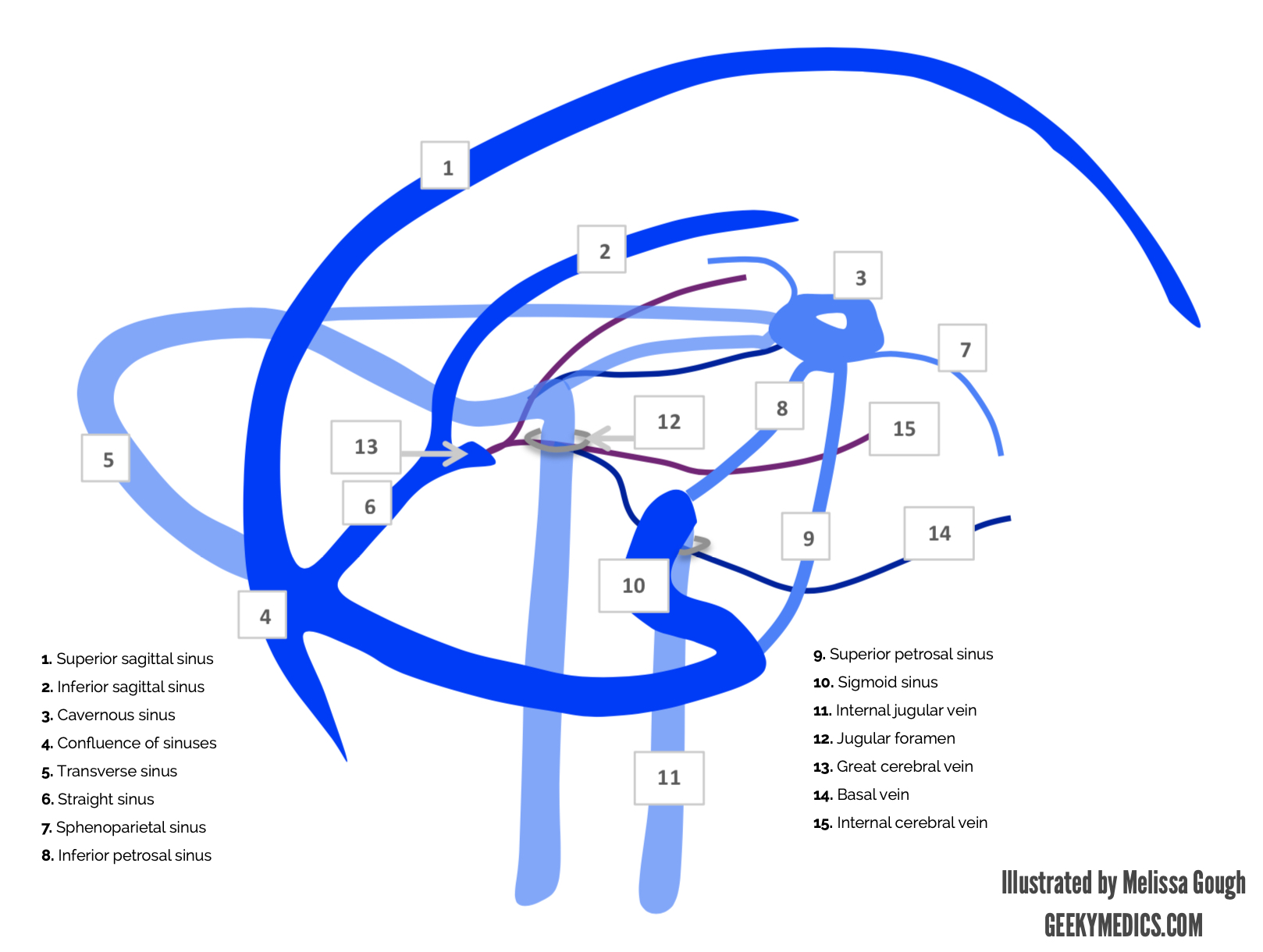
Apr 12, 19 · The term cavernous sinus was first used by Winslow in 1734 owing to the multiple filaments, or septa, within, which gave it a cavernous or plexiform appearance However, this term has courted controversy because the cavernous sinus has certain anatomic differences from other dural venous sinusesGamma Knife Treatment for Dural Malformations Dural malformations, with or without associated AVM's are uncommon lesions Optimal treatment is unknown at this time, however reasonable cure rates can be achieved with smaller lesions using Gamma surgery Larger lesions, unless wholly inoperable, should be managed with at least partial open surgical or endovascular treatment priorDural folds made of invaginations of dura mater into crevices of the brain Superior sagittal sinus sigmoid sinus transverse sinus occipital sinus confluence of sinuses inferior sagittal sinus straight sinus




Dural Venous Sinuses Summaries For Medical Students



Easy Notes On Venous Drainage Of The Brain Learn In Just 3 Mins Earth S Lab
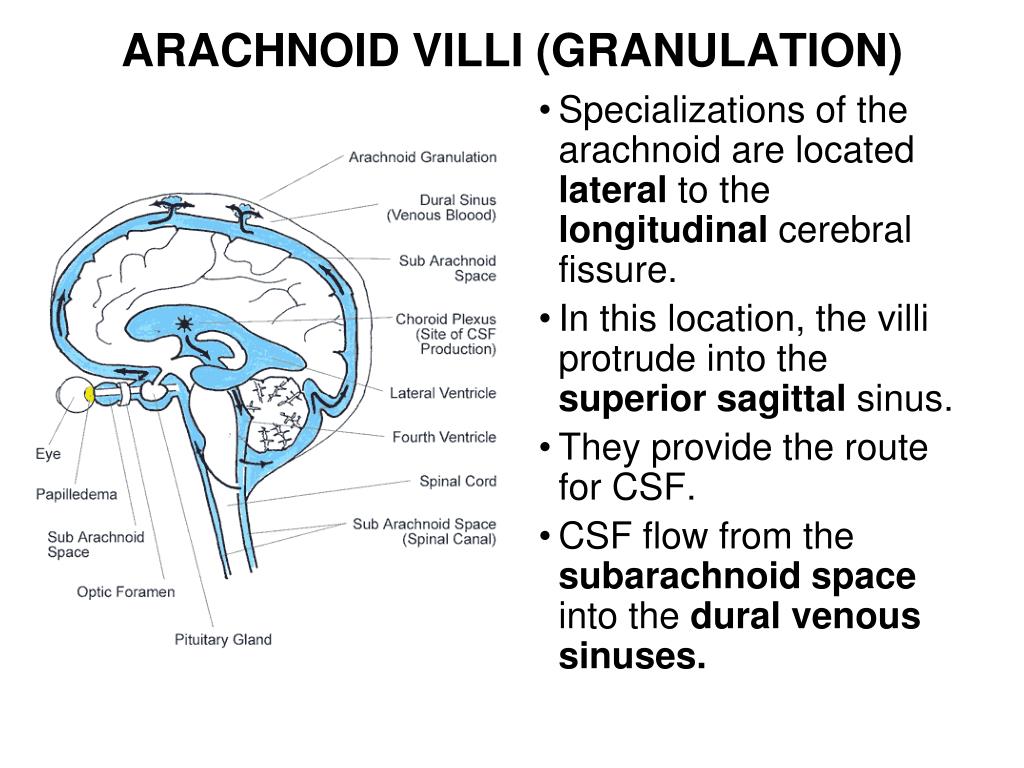
Definition Dural sinus thrombosis is a circulatory abnormality of the dural sinuses characterized by thrombosis usually caused by a hypercoaguable state occurring in conditions such as protein C or protein S deficiency, use of oral contaraceptives, polycythemia vera nephtrotic syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, and collagen vascularJun 28, 21 · The arachnoid granulations (Pacchionian bodies) are protrusions of the arachnoid mater that pierce the meningeal dura and protrude into the lumina of the dural venous sinusesThe core of each arachnoid granulation is continuous with the subarachnoid space, therefore, containing the cerebrospinal fluid The CSF diffuses through the lining of the arachnoid granulations into the dural venous sinusesNov 05, 18 · The occipital sinus is the smallest dural venous sinus, receiving tributaries from the margins of the foramen magnum It runs along the inner surface of the occipital bone and may anastomosis with the sigmoid sinuses and posterior internal vertebral plexus that drain into the torcular Herophili 10



Ispub Com Ijns 4 2 6019




The Torcular Herophili Confluence Of Sinuses Sciencedirect
Jan 01, 12 · Dural sinus malformation (DSM) is an extremely rare and congenital cerebrovascular malformation that is associated with dural arteriovenous fistula and a large dural lake, which may mimic the clinical malformations of an infantile dural arteriovenous shunt or the vein of Galen




Venous Connections Of The Cavernous Sinus In Axial View Download Scientific Diagram



Dural Venous Sinuses Wikipedia
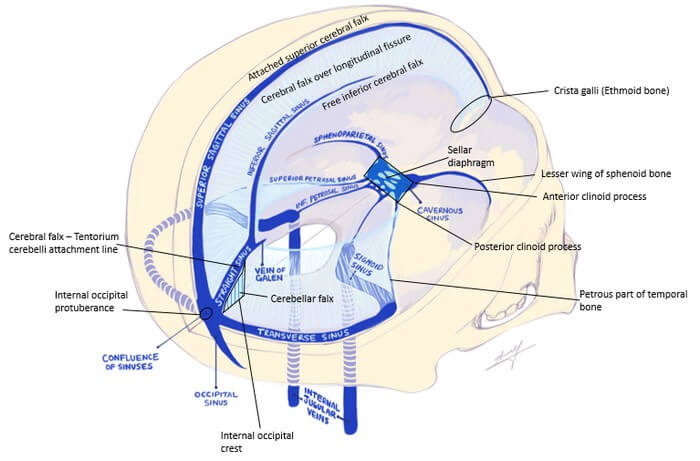



Dural Reflections And Venous Sinuses Epomedicine




Flowchart Blood Supply To The Brain And Venous Sinus Drainage Of The Brain On Meducation
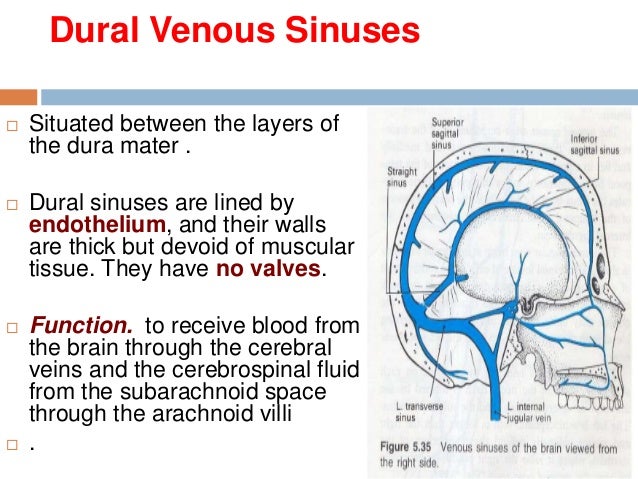



15 Dural Venous Sinuses




Cranial Meninges Clinical Gate




Cavernous Sinus Dural Venous Sinus Youtube




Cerebral Venous Thrombosis A Practical Guide Practical Neurology
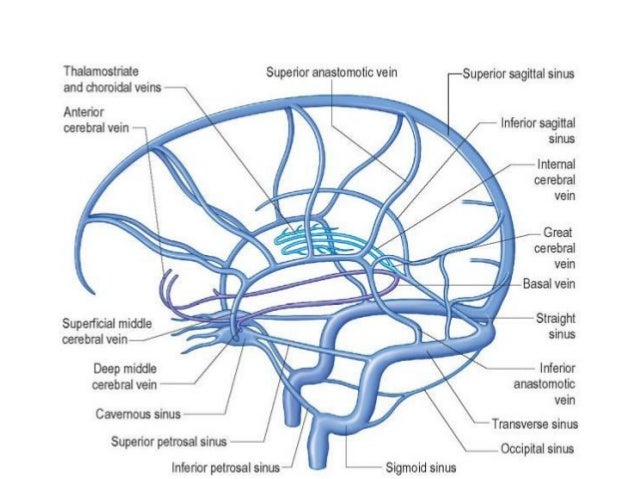



Dural Venous Sinuses
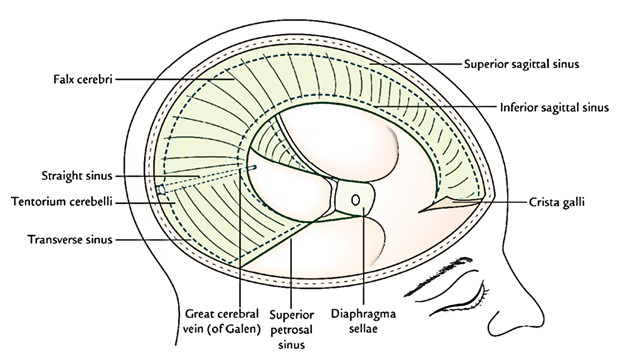



Easy Notes On Dura Mater Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177 x



Print Ventricles Meninges Csf And Blood Vessels Of The Brain Flashcards Easy Notecards




Pin On Internal Medicine




Anatomical Diagrams Of The Brain




Big Sexy Brain
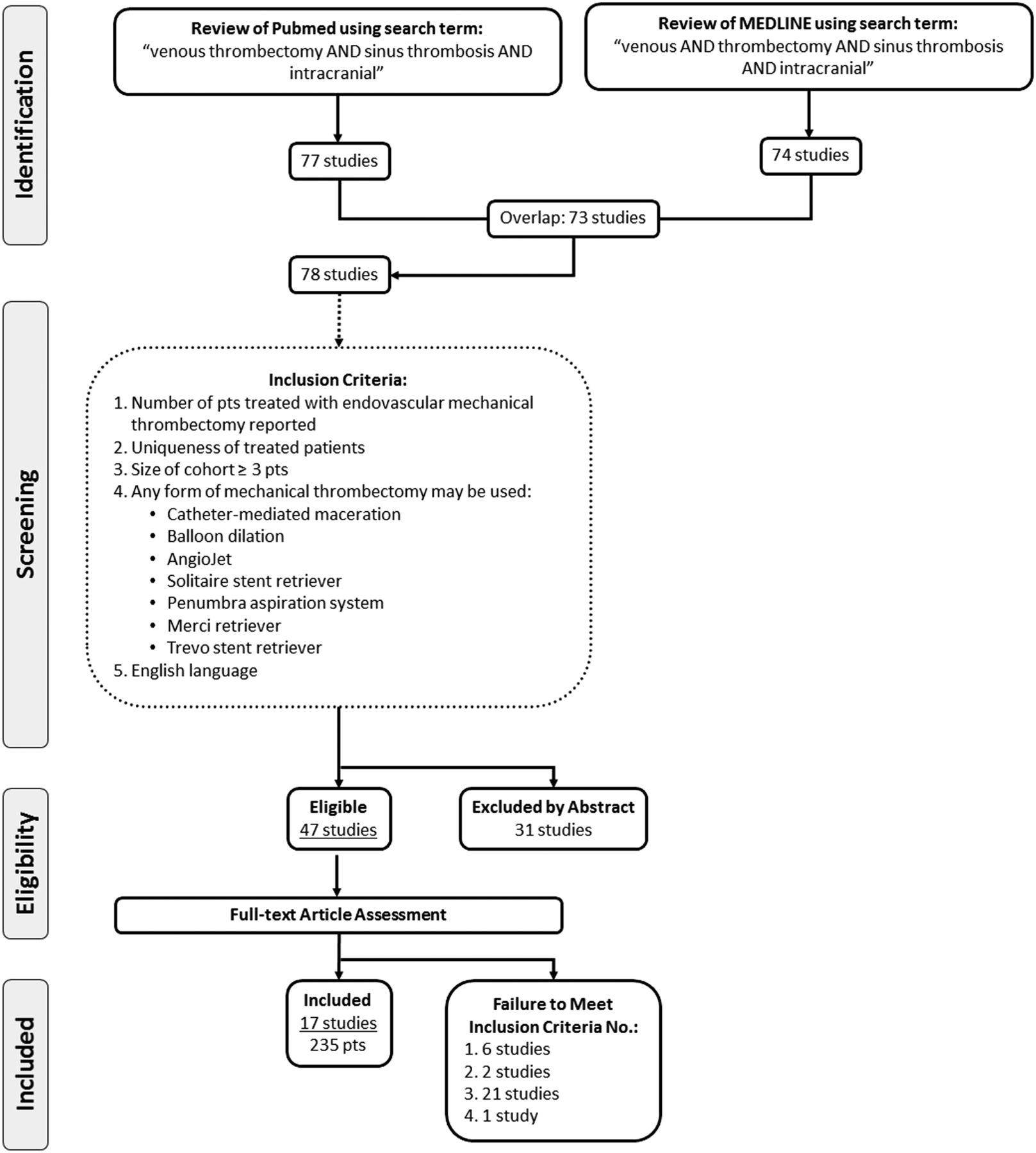



Endovascular Mechanical Thrombectomy For Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis A Systematic Review Journal Of Neurointerventional Surgery




Inferior Petrosal Sinus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Physiologic Change In Flow Velocity And Direction Of Dural Venous Sinuses With Respiration Mr Venography And Flow Analysis American Journal Of Neuroradiology




Examination Of The Neck Veins Nejm
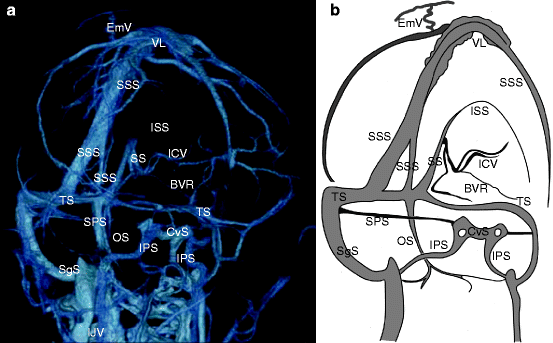



Normal Anatomy Of Intracranial Veins Demonstration With Mr Angiography 3d Ct Angiography And Microangiographic Injection Study Springerlink




The Superior Sagittal Sinus Sciencedirect




Pin On Step 1



Easy Notes On Dura Mater Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab




A Descriptive Study Of Venous Sinus Pressures And Gradients In Patients With Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Journal Of Neurointerventional Surgery



Sinus Venous High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



The Cavernous Sinus Contents Borders Thrombosis Teachmeanatomy




Dural Venous Sinuses Diagram Quizlet



Venous Sinuses Neuroangio Org



1




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Cavernous Sinus Draw It To Know It Neuroanatomy Youtube




Schematic View Of Different Stages Of Cerebral Venous Thrombus On Download Scientific Diagram



Venous Drainage Of The Brain Anatomy Geeky Medics



Ppt Central Nervous System Peripheric Nervous System Powerpoint Presentation Id



Dural Venous Vasculature Intrinsic Dural And Skull Veins Neuroangio Org




A Schematic Illustration Of The Cranial View Of A Mouse Brain The Download Scientific Diagram




Arachnoid Granulation Operative Neurosurgery




The Repair Of Dural Venous Sinus Wounds By Autogenous Venorrhaphy In Journal Of Neurosurgery Volume 35 Issue 4 1971



1
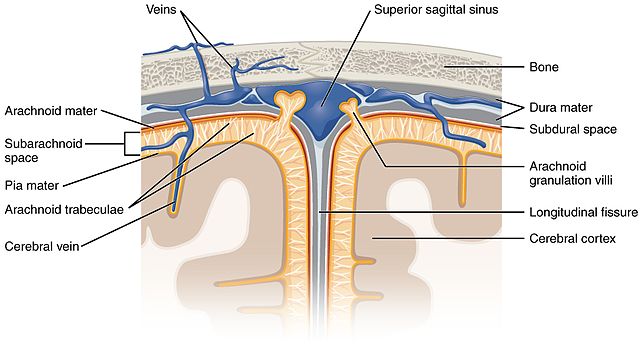



Anatomy And Function Of The Dural Venous Sinuses Medical Library
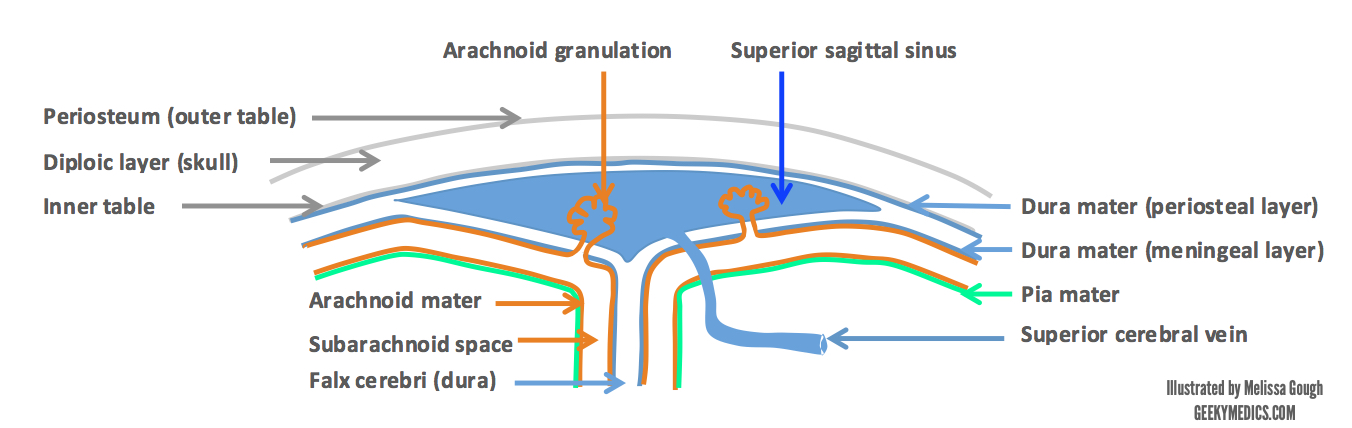



Venous Drainage Of The Brain Anatomy Geeky Medics




Chapter 23 Outline Anatomy Of Blood Vessels Blood



Imagequiz Dural Venous Sinuses



Venous Drainage Of The Brain Mednotes



Dural Venous Vasculature Intrinsic Dural And Skull Veins Neuroangio Org
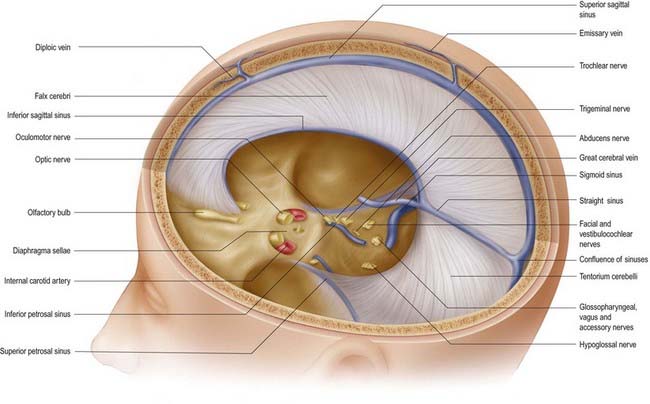



Cranial Meninges Clinical Gate




Dural Venous Sinuses Wikipedia




The Transverse Sinus Sciencedirect



Q Tbn And9gcrm9v 1gnxmftbphkc Md2a02f5qna7fmjfvo4ibsqvxk8frpes Usqp Cau




Dural Venous Sinuses Of The Brain Diagram
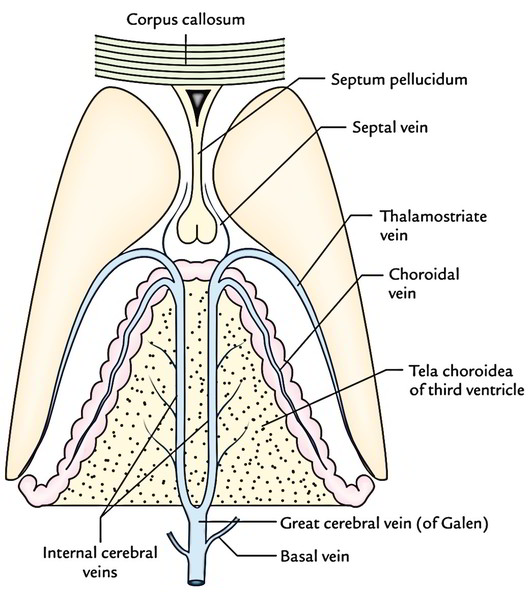



Easy Notes On Venous Drainage Of The Brain Learn In Just 3 Mins Earth S Lab




Pdf A Review Of Extraaxial Developmental Venous Anomalies Of The Brain Involving Dural Venous Flow Or Sinuses Persistent Embryonic Sinuses Sinus Pericranii Venous Varices Or Aneurysmal Malformations And Enlarged Emissary Veins



Meninges And Dural Folds Mednotes
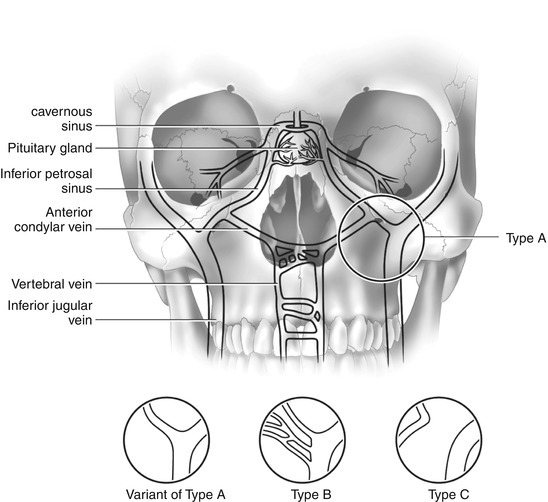



Petrosal Venous Sinus Sampling Radiology Key
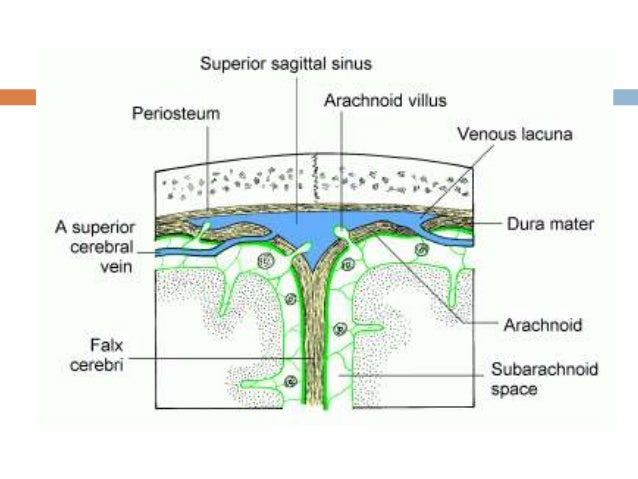



15 Dural Venous Sinuses




Ppt Central Nervous System Peripheric Nervous System Powerpoint Presentation Id




Cavernous Sinus Structure Function Youtube




Dural Venous Sinuses Paired And Unpaired Venous Sinuses Anatomy Qa



Cisterns Sinuses Veins Neuroanatomy Flashcards Draw It To Know It
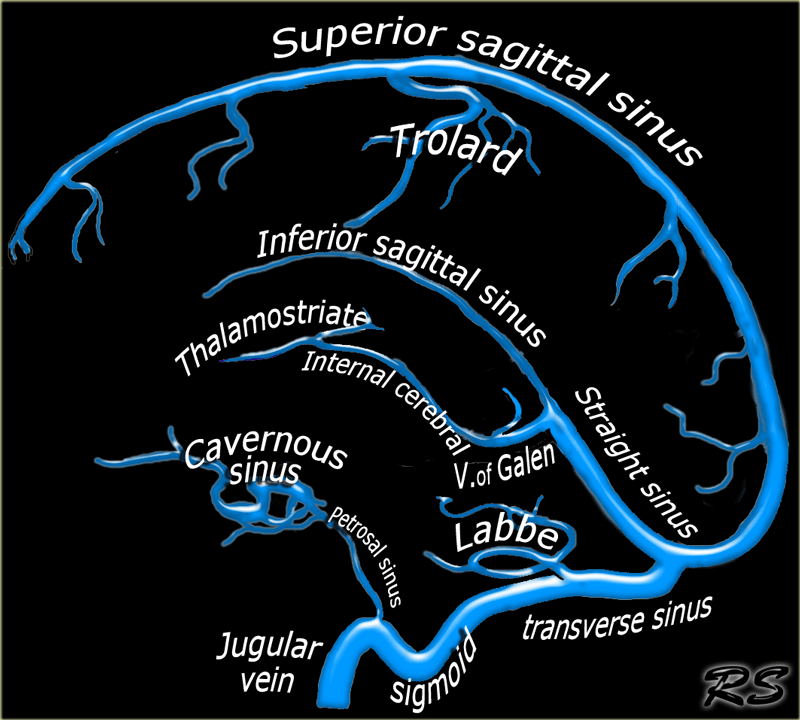



The Radiology Assistant Cerebral Venous Thrombosis




Dural Venous Sinuses Paired And Unpaired Venous Sinuses Anatomy Qa



Venous Drainage Of The Brain Mednotes
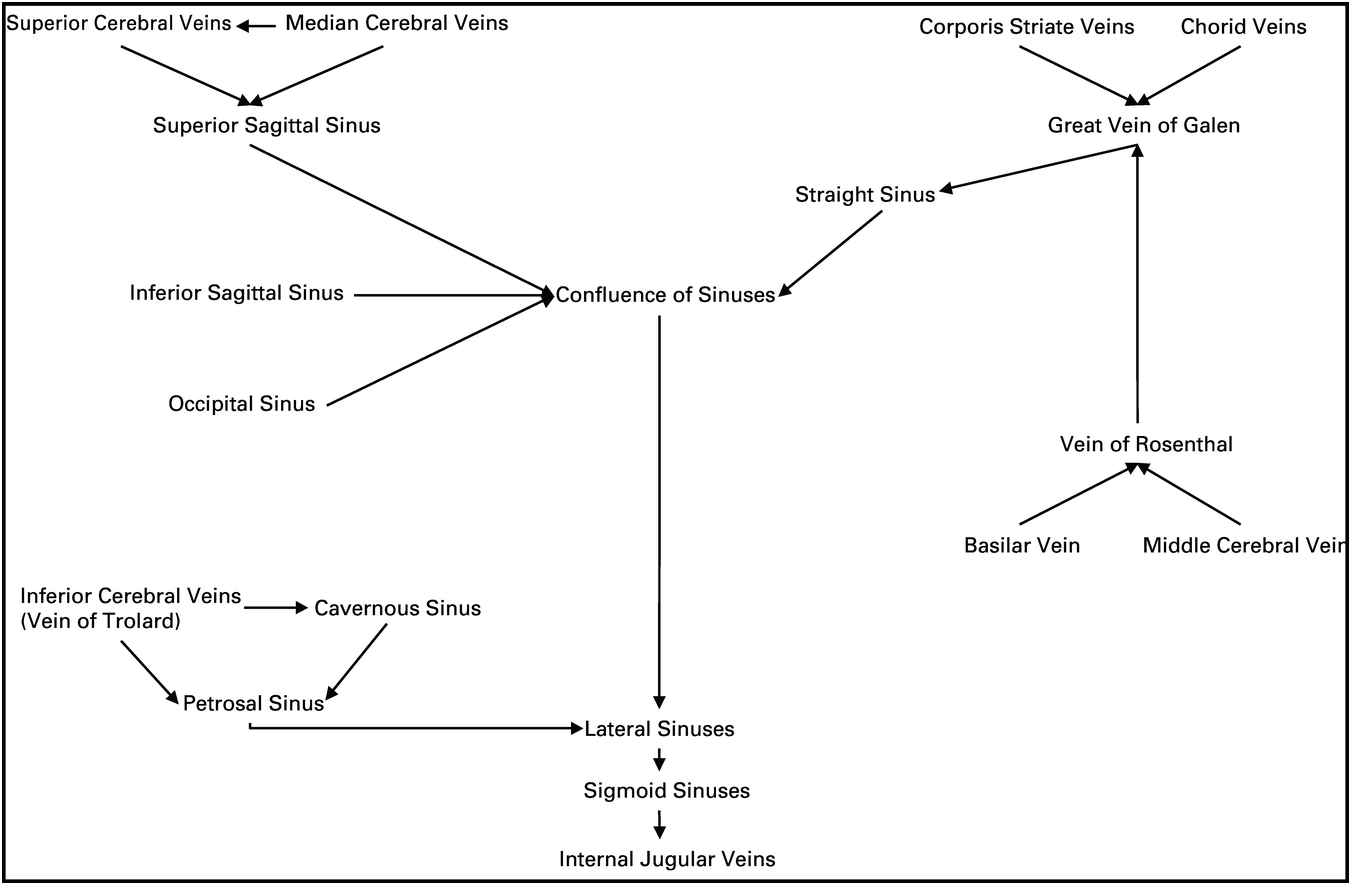



Management Of Stroke Patients Section Iv The Stroke Book




Ppt Central Nervous System Peripheric Nervous System Powerpoint Presentation Id




Dural Venous Sinuses Youtube




Dural Venous Sinuses Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
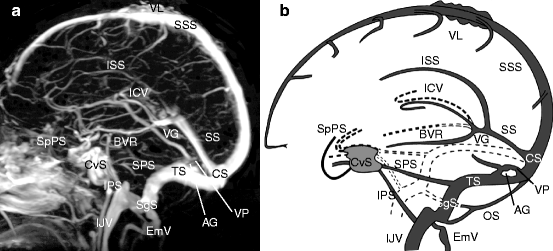



Normal Anatomy Of Intracranial Veins Demonstration With Mr Angiography 3d Ct Angiography And Microangiographic Injection Study Springerlink




Borden Classification Operative Neurosurgery
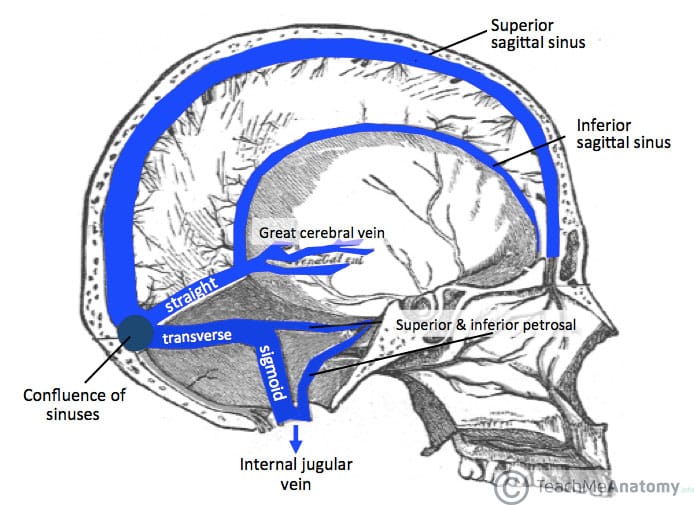



Venous Drainage Of The Cns Cerebrum Teachmeanatomy




Pdf Cerebral Venous Anatomy
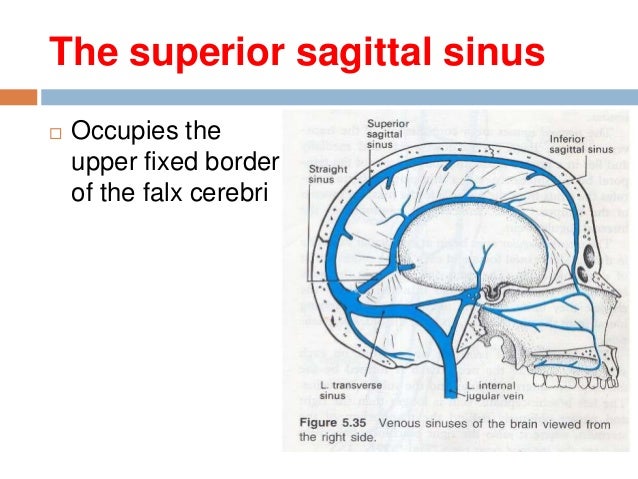



15 Dural Venous Sinuses




Cerebral Circulation And Metabolism Sciencedirect



1



Venous Sinuses Neuroangio Org




Pin On Neuro




Dural Venous Sinuses Medmule




Reflecting On Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis And The U S Presidential Election The Stroke Blog



2




Unpaired Dural Venous Sinuses Situation Tributaries Communications Confluence Of Sinuses Youtube




A Microcontroller Based Simulation Of Dural Venous Sinus Injury For Neurosurgical Training In Journal Of Neurosurgery Volume 128 Issue 5 17
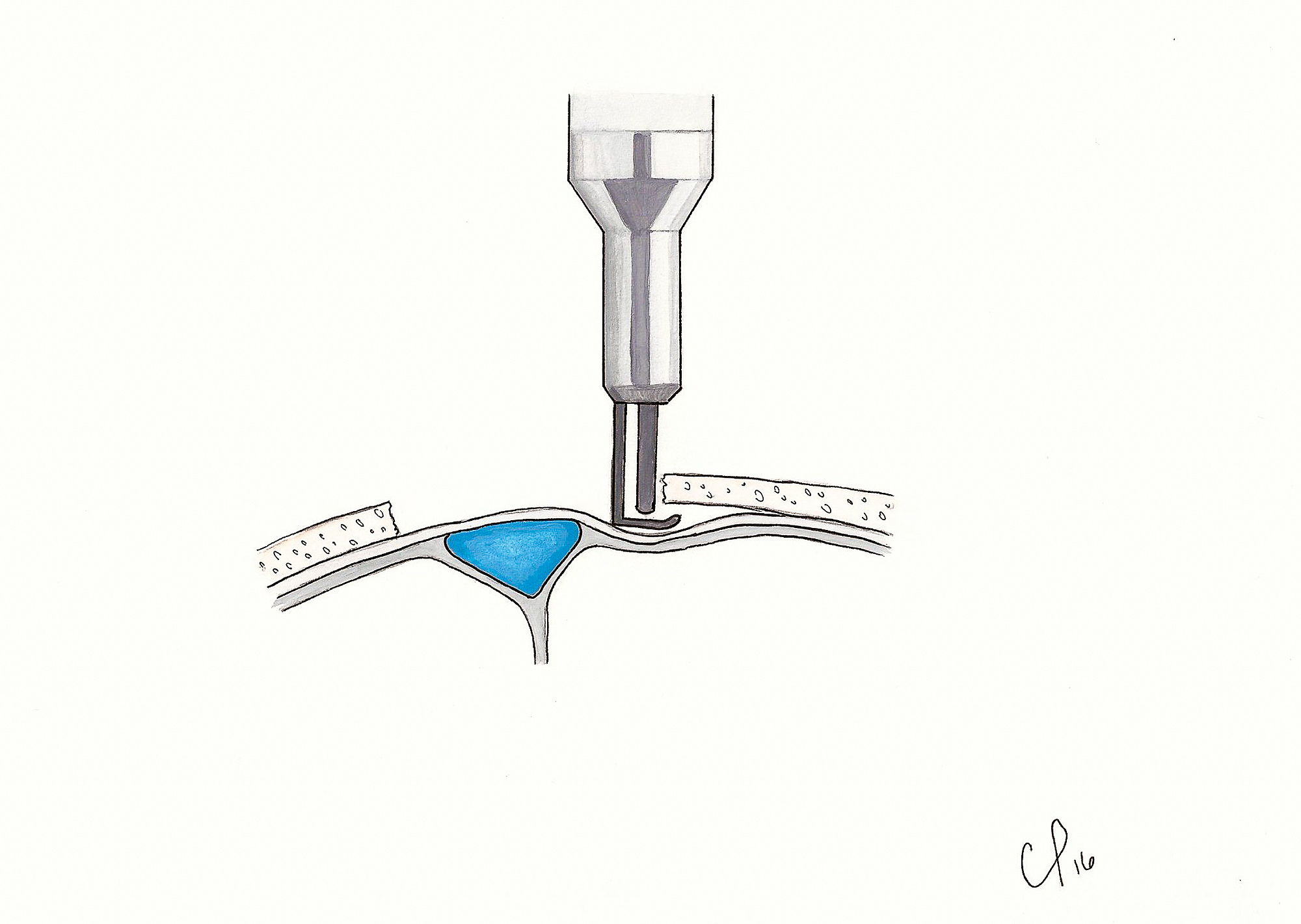



Cureus Exposure Of Dural Venous Sinuses A Review Of Techniques And Description Of A Single Piece Troughed Craniotomy



Http Www Liebertonline Com Doi Pdf 10 10 Ham 11 1026


コメント
コメントを投稿